Safety:
As safe as traditional open surgeries. Minimal blood loos, pain, blood transfusion, only overnight hospital stay.
Length Of The Surgery:
Depends on the type of Nephrectomy performed
When to approach your Urologist?:
- Blood passing through urine.
- Constant fevers without any known source of infection.
- Frequent pain in the lower back, waist or abdomen.
- Sudden weight loss.
- Early fatigue.
- Formation of abdominal lumps.
- Loss of appetite.
- Pertaining swelling of ankles and legs.
- At the later stage of cancer:
- Shortness of breath
- Coughing up blood
- Bone pain
Types Of Kidney Cancer:
Transitional cell carcinoma, cells in a certain part of a kidney (almost always in the tubular linings) turn malignant and begin to spread and start to form a tumor.
Hypernephroma/ adenocarcinoma is the kidney cancer type that is seen commonly in adults mostly above 40 years of age.
In children, Wilms tumor is seen to commonly occur.
Kidney Cancer Diagnosis:
- Physical examination
- Urine tests
- Blood test
- Intravenous Pyelogram (IVP)
- CT scan
- Ultrasound test:
- Biopsy
- Surgery
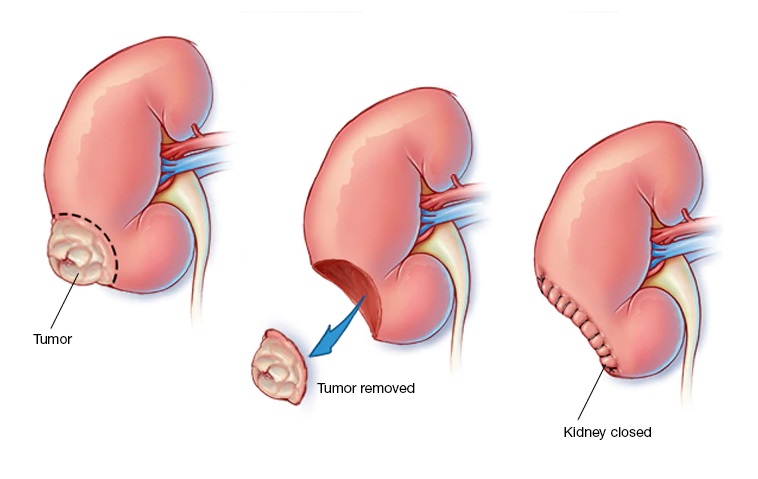
Treatment For Kidney Cancer:
Nephrectomy surgery is used to treat renal cancers by organ removals.
- Radical (Complete) nephrectomy: In this type of nephrectomy, the entire kidney is removed.
- Partial nephrectomy: In such cases, only the diseased or affected tissue from the kidney is removed. The healthy tissue is kept intact.
Preparation:
Certain medications to be specifically avoided pre surgery:
- Aspirin.
- Ibuprofen Motrin.
- Voltaren, Plavix, Lovenox, Vioxx, Celebrex.
- Advil, Ticlid, Alka Seltzer, Coumadin, Vitamin E.
- Arthritis medications: avoided since before a week of the surgery otherwise it can cause bleeding during the surgery.
- The urine culture analysis should be negative.
- In case of UTI Urinary Tract Infection, it should be treated before the surgery by prescribed antibiotics.
- In case of history severe lung/ heart conditions, blood pressure, diabetes, it is advisable not to perform nephrectomy on the patient.
Nephrectomy Procedure:
- Nephrectomy is carried out under general anesthetic.
- A urinary catheter is inserted to drain the bladder of the urine.
Types of Nephrectomy Surgeries: - Open surgery: An incision about 25 to 35 cms is made in the abdomen or on the side between lower ribs near the affected kidney area. For better access to the kidney, the lower rib may have to be removed.
- Laparoscopic surgery: A few incisions (very small) are made in the abdomen and small surgical tools with a video camera are inserted. A slightly larger opening is done for total nephrectomy.
- Robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery: Robot-assisted surgery wherein the robotic instruments are controlled by the surgeon via the operating interface, requires even smaller incisions and provides better quality imaging and facilitates precise and accurate removal.
Nephrectomy Complications:
Nephrectomy risks include:
- Need for open surgery.
- Bleeding.
- Fever.
- Nausea.
- Constipation.
- Fatigue.
- Urinary abnormalities.
- Infection.
- Lower body aches.
- Organ/ Tissue Injury
Follow- up:
It’s usually recommended that someone stays with you for the first 24 hours after surgery. This is in case you experience any symptoms that suggest there could be a problem, such as:
- 24 to 48-hour surveillance.
Visit the doctor: - Removal of urinary catheters in one or two days of surgery.
- Caring for your remaining kidney:
- Have a light healthy diet with limited salt intake
- Avoid high protein diet, alcohol and caffeine
- Avoid strenuous activity and exercise for several weeks.
- Monitor urine protein levels and glomerular filtration rate.
- Emergency Follow up:
- Chest pain/ breathing difficulty.
- Vomiting/ nausea
- Blood pressure
All the above, treatments are finalized taking into consideration the overall health, severity, age and other ailments of the patient. Only a well-experienced urologist should perform the above treatment.